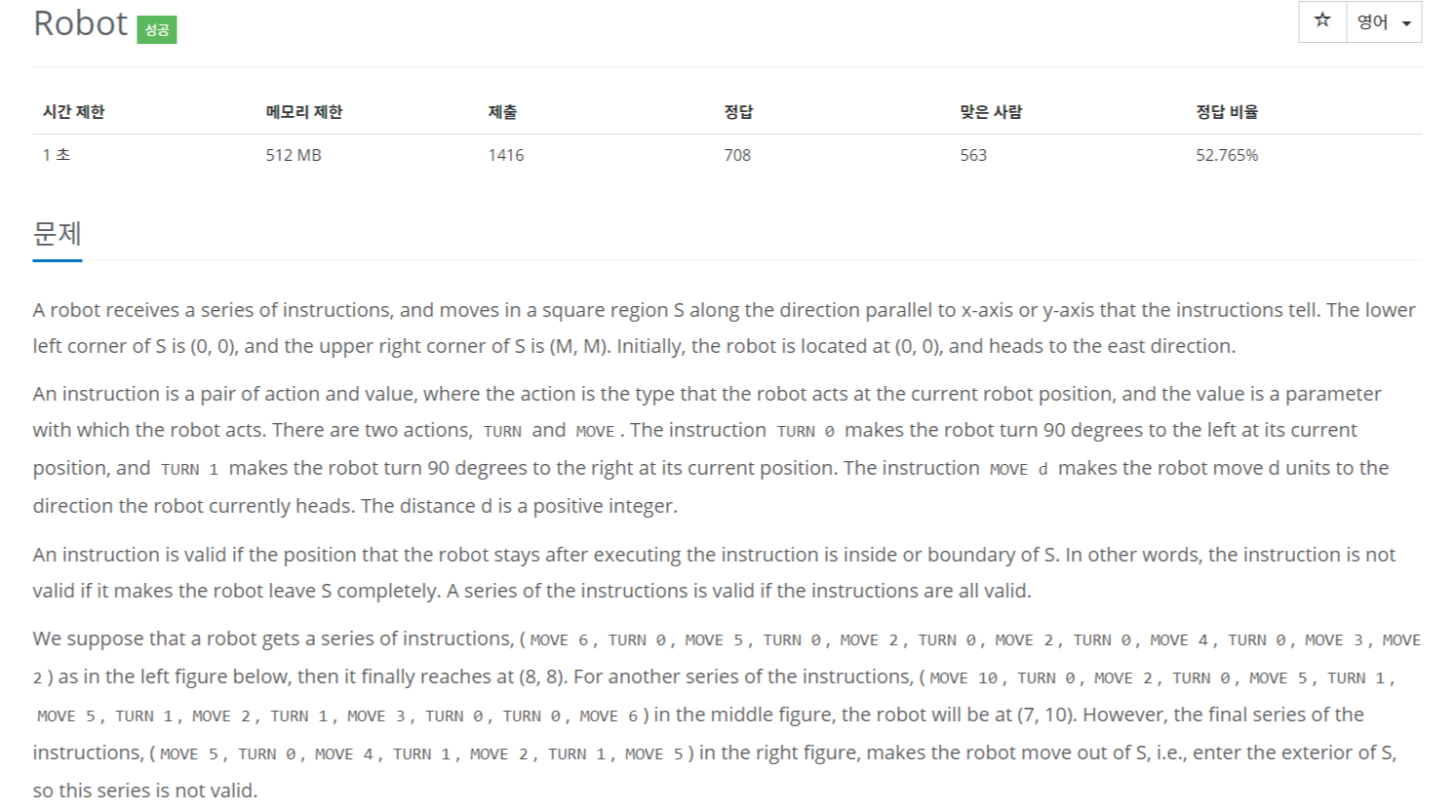
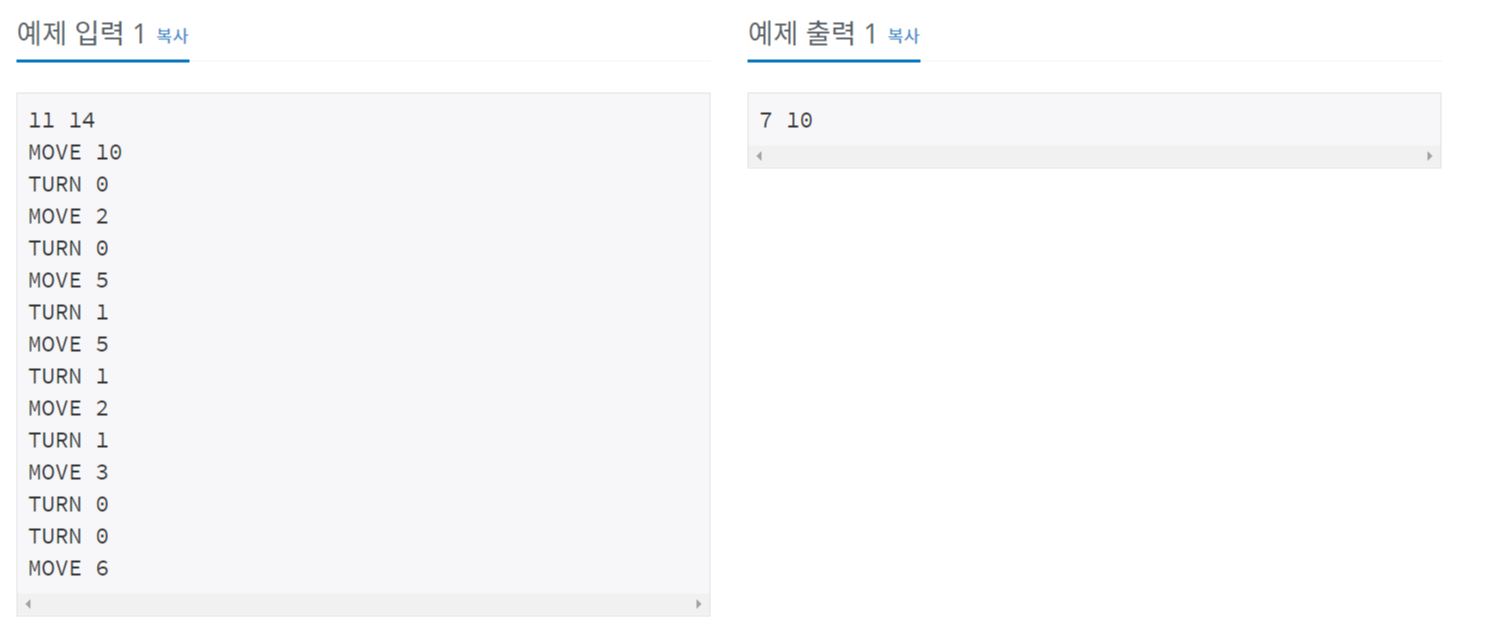
안녕하세요
여행벌입니다.
오늘은 ACM-ICPC 2015 본선 문제인
BOJ 11592번 3-Primes Problem 문제를 다뤄보도록 하겠습니다.


[문제해석]
7 ~ 1000 사이의 양수가 주어졌을 때, 이 양수를 3개의 소수의 합으로 표현할 수 있다면, 3개의 소수를 출력하고, 아니라면 0을 출력하는 알고리즘을 작성하여라.
[알고리즘설계]
1. 에라토스테네스 체를 이용하여 1 ~ 1000 사이의 소수를 먼저 찾는다.
2. 3중 포문을 이용해 주어진 양수(ninput)를 3개의 소수의 합으로 판단할 수 있는지 없는지 판단한다.
* Input 값의 범위가 1000 으로 매우 작다. 따라서, 무식하게 3중 포문을 이용해서 푸는 것이 빠르겠다고 판단하였다.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
// 에라토스테네스체로 prime부터 찾자.
bool prime[1001];
for (int i = 0; i < 1001; i++)
prime[i] = true;
for (int i = 2; i * i <= 1000; i++) {
if (prime[i] == true) {
for (int j = 2 * i; j <= 1000; j += i) {
prime[j] = false;
}
}
}
int test_case;
cin >> test_case;
for (int i = 0; i < test_case; i++) {
int ninput, j , k , l;
cin >> ninput;
for (j = 2; j < 1000; j++) {
for ( k = 2; k < 1000; k++) {
for ( l = 2; l < 1000; l++) {
if (j + k + l > ninput)
break;
if (prime[j] && prime[k] && prime[l] && j + k + l == ninput){
cout << j << ' ' << k << ' ' << l << '\n';
break;
}
}
if (prime[j] && prime[k] && prime[l] && j + k + l == ninput) {
break;
}
}
if (prime[j] && prime[k] && prime[l] && j + k + l == ninput) {
break;
}
}
if (prime[j] && prime[k] && prime[l] && j + k + l == ninput) {
continue;
}
else
cout << 0 << '\n';
}
return 0;
}input이 작아서 문제에 쉽게 접근할 수 있었지만, input이 크다면 접근하기 어려울 것 같다.
'Problem Solving > ICPC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [ACM-ICPC][BOJ] 13560 - Football Game 문제풀이 (0) | 2019.07.24 |
|---|---|
| [ACM-ICPC][BOJ] 11497 - Log Jumping 문제풀이 (0) | 2019.07.23 |
| [ACM-ICPC][BOJ] 13567 - ROBOT 문제풀이 (0) | 2019.07.21 |
| [ACM-ICPC][BOJ] 13565 - Percolation 문제풀이 (0) | 2019.07.21 |
| [ACM-ICPC][BOJ] 16360 - Go Latin 코드반성 (0) | 2019.07.19 |